Source: IWA Journal
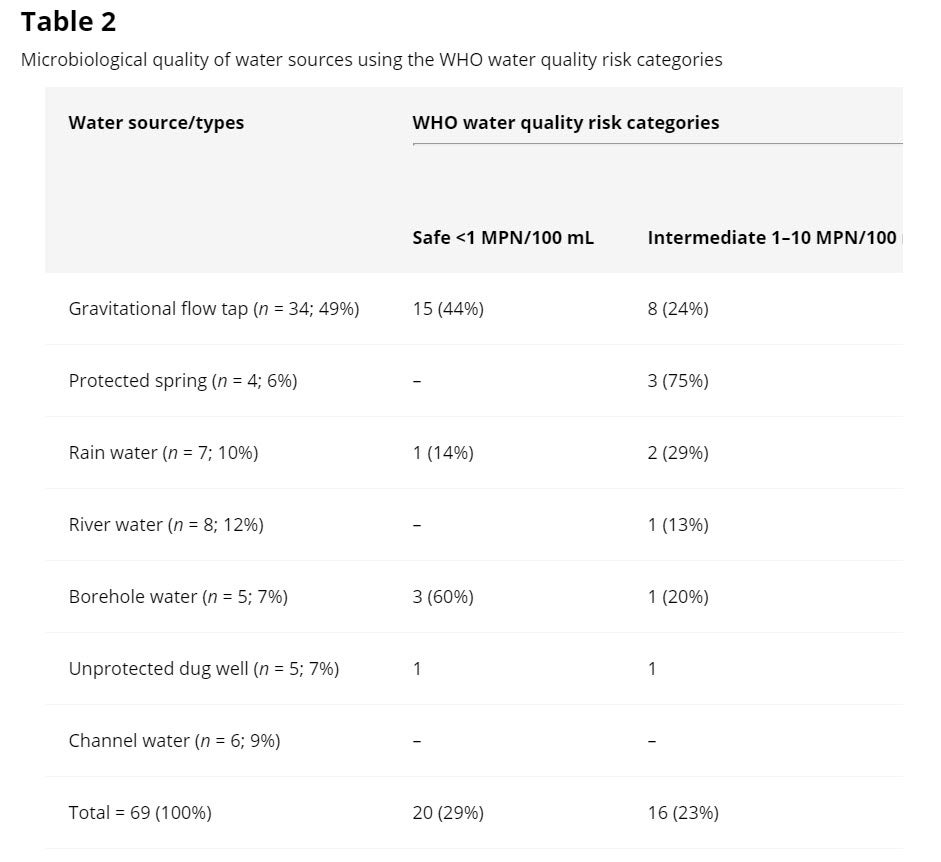
A new study published in the IWA Journal of Water, Sanitation & Hygiene assessed the bacteriological quality of water sources in two rural areas of Uganda using the Aquagenx Compartment Bag Test (CBT). A total of 200 water samples were collected from 69 different water sources.
The authors write, ” The CBT was found to be robust and easy to use in all field situations…The CBT performs just as efficiently as the standard method, membrane filtration for the detection of E. coli in drinking water, thereby predicting the risk of waterborne disease. In developing countries such as Uganda where resources for water quality testing are limited, this valuable test can be used by the public health officers in aiding the prevention of diarrheal disease and reducing the burden of disease. The CBT has the potential of being employed in monitoring activities of the microbial water quality where there are excessive microbial levels detected in drinking water and used to support the water safety plan (Wang 2015).”


